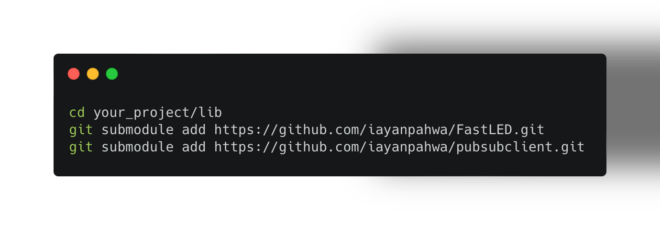
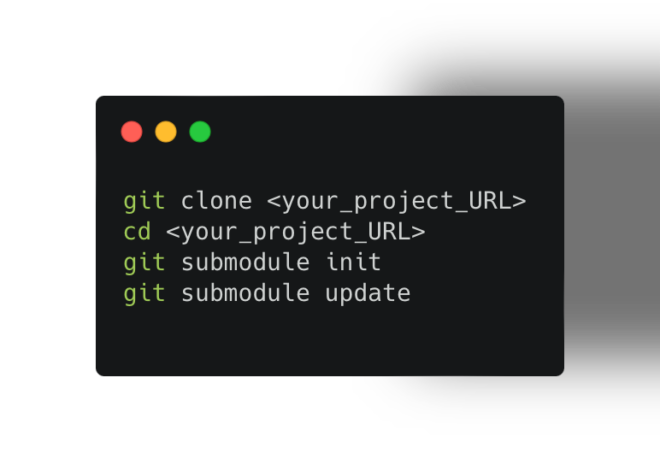
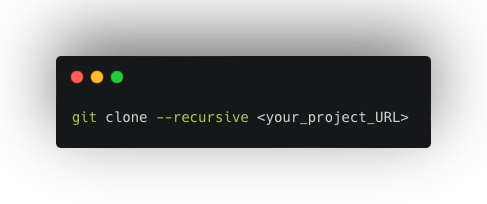
Collaboration is key in the world of Git version control. But keeping track of changes from multiple developers can get tricky. This blog post dives into two essential Git features—remotes and cherry-pick—that empower you to streamline your workflow and effectively manage contributions.
{{ advertisement }}
Understanding Git Remotes: A Bird’s Eye View
By default, your GitHub repository typically has a single remote—the origin, representing the main repository you cloned from. However, in larger projects with multiple developers, things get more interesting. Often, developers create personal forks before they push their code.This allows them to work on a separate copy of the code base, and once they are satisfied with the changes, they can merge back into the main codebase.
Here’s where remotes come into play. They are references to additional copies of your Git repository, potentially containing valuable contributions from other developers.
NEW Developer Nation survey is live! Participate, shape the trends in software development, and win big. Start here!
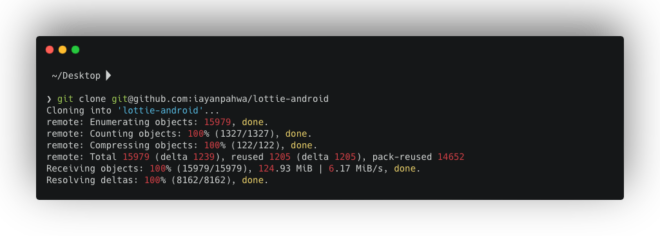
Let’s use an Open-Source project: Lottie
Imagine we’re working with the fantastic Lottie by Airbnb, a library that renders After Effects animations on mobile platforms. We’ve cloned a fork (iayanpahwa/lottie-android) and want to explore changes made by other contributors to lottie (gpeal and felipecsl).
Adding Remotes: Reaching Out to Other Forks
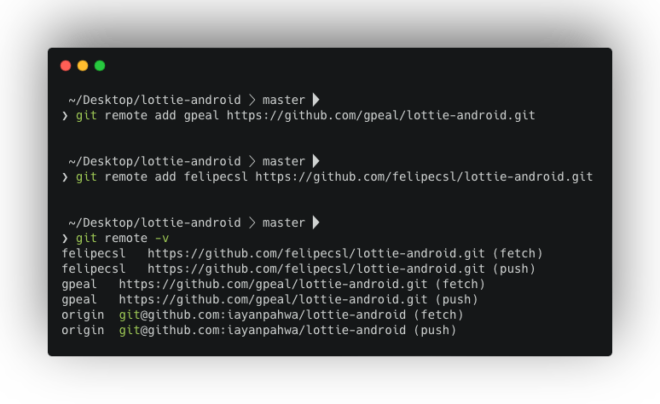
To access these developers’ workspaces, we can add them as remotes using the git remote add command:
git remote add <remote_name> <repository_URL>For example:
git remote add gpeal https://github.com/gpeal/lottie-android.gitgit remote add felipecsl https://github.com/felipecsl/lottie-android.gitNow, using git remote -v, you can see all configured remotes, including their URLs.
Fetching the Goods: Downloading Changes
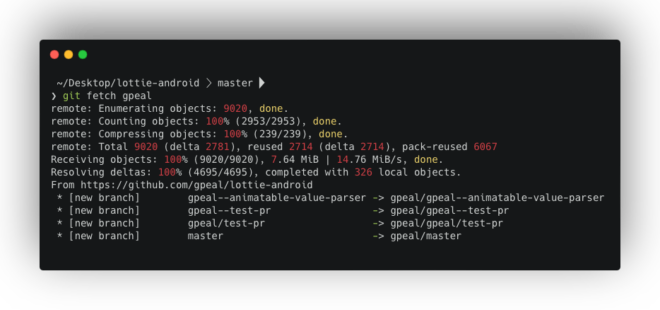
With remotes in place, we can retrieve changes from other contributors using git fetch.
- Fetching from a specific remote:
- Fetching from all configured remotes:
git fetch --allThis downloads the commits made by these developers without integrating them into your local working directory yet.
git cherry-pick: Borrowing the Best Bits
Git cherry-pick allows you to meticulously select and apply specific commits from other branches (including those fetched from remotes) onto your current branch. This is particularly useful for integrating contributions from multiple developers, testing them individually, or incorporating specific fixes.
A Real-World Cherry-picking Scenario
Imagine you manage an open-source project that receives a wave of pull requests. You might want to test these contributions together before merging them. Here’s how cherry-picking can help:
Create a New Branch:
git checkout -b my-test-branch- Fetch Necessary Code (if not already done): Use
git fetchas explained earlier. - Cherry-picking Commits: Once you have access to the desired commits, cherry-pick them one by one using their commit hashes:
git cherry-pick <commit_hash>For instance, to test a specific commit (648c61f5275998c461347b5045dc900405306b31) by contributor gpeal:
git cherry-pick 648c61f5275998c461375647845dc900405306b31 [ commit made by gpeal ] This brings gpeal’s changes to your my-best-branch for isolated testing.
Remember: Cherry-picking can rewrite history, so use it cautiously. Always create a dedicated branch for testing before integrating changes into your main codebase.
Wrapping Up:
By mastering remotes and cherry-pick you can effectively collaborate on Git projects, leverage valuable contributions from others, and ensure a smooth and efficient development workflow.
Feel free to reach out with any questions! Happy coding! Do check our blogs on git internals for more learning:
- How Git Submodules Can Save You Time
- Git Internals Part 1- List of basic Concepts That Power your .git Directory
- Git Internals Part 2: How does Git store your data?
- Git Internals Part 3: Understanding the staging area in Git
NEW Developer Nation survey is live! Participate, shape the trends in software development, and win big. Start here!